 What does your immune system do, exactly? Think of your immune system as your natural defense against infection. That is a very simplistic definition, since the way your body fights sickness and disease is incredibly detailed and interconnected. But for a short definition which gets to the point, that is right on the money.
What does your immune system do, exactly? Think of your immune system as your natural defense against infection. That is a very simplistic definition, since the way your body fights sickness and disease is incredibly detailed and interconnected. But for a short definition which gets to the point, that is right on the money.
Each person’s natural defense system is composed of the following “lines of defense”:
The 1st Line of Defense – Mechanical and Physical Barriers
This is the first layer of your immune system, the very first thing that infection and disease encounter. This includes the cornea of your eyes, your skin, and membranes which line your reproductive, digestive, urinary and respiratory systems.
When this 1st line of defense is healthy, it is difficult (but not impossible) for infection to occur.
The 2nd Line of Defense – White Blood Cells (leukocytes)
Leukocytes are your white blood cells. They travel through your bloodstream and into your tissues. Their job? To attack unhealthy microorganisms and foreign invaders. They are present in 3 subcategories – granulocytes, monocytes and lymphocytes. Granulocytes make up anywhere from 50% to 60% of all your white blood cells.
The 3rd Line of Defense – Molecules
There are certain molecules in your body that influence the behavior of other immune system cells. These include antibodies, proteins and cytokines. You can consider the cytokines as the “messengers of the immune system”. They spread the word about possible infection and attack. These molecules are not located inside your cells. They are located in certain body fluids such as plasma.
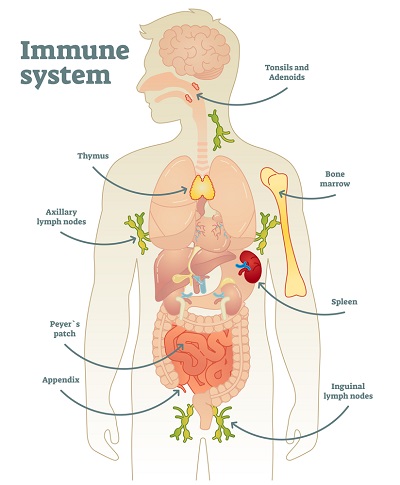
The 4th Line of Defense – Organs
Your immunity system includes both primary and secondary lymphoid organs. Your bone marrow and thymus (primary lymphoid organs) produce and increase your number of white blood cells. Your secondary lymphoid organs include your tonsils, appendix, lymph nodes, spleen and small intestine Peyer patches.
When your immune system is working properly, it first recognizes an attempt at an unhealthy invasion. Then it activates your defense system, mobilizing and attacking the invaders. Next it works to regulate its response properly, resolving the attack by eliminating infection and disease from your body.
This quickly explained process is very detailed, powerful and yet delicate. Cutting down on stress in your life, exercising regularly and getting plenty of sleep can all help boost your immunity system health.
Eating foods rich in antioxidants, like parsley, asparagus and avocados, and getting plenty of vitamin D from sunshine or supplementation are 2 other important measures that contribute to a healthy immune system.






