Autoimmune Disorders
 Alopecia areata is a skin condition which occurs as a result of our immune system mistakenly attacking our own healthy tissues. This creates a condition called autoimmune disease.
Alopecia areata is a skin condition which occurs as a result of our immune system mistakenly attacking our own healthy tissues. This creates a condition called autoimmune disease.
Autoimmune disease can present itself in different ways, depending on which body part is affected. When the immune system damages the hair follicles the result is hair loss.
One or more bald patches appear on the scalp. These patches are usually round in shape and the size of a large coin. Occasionally the beard, eyebrows, eyelashes or other body hair are also affected.
Alopecia areata can occur at any age. However it usually affects children, teenagers and young adults. Research shows that the first attack of this disease usually happens before the age of 30.
The Effects of Alopecia Areata
There is no scarring or physical pain associated with the condition, and the affected hair follicles are not destroyed. Often as one patch is regrowing another patch is appearing. Apart from the bald patches the scalp usually has a healthy appearance. Continue reading
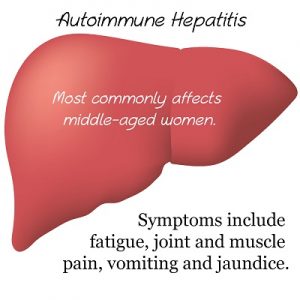 When white blood cells (lymphocytes) erroneously attack liver cells, they cause inflammation and damage to the liver. This results in the condition autoimmune hepatitis. There are two types of autoimmune hepatitis.
When white blood cells (lymphocytes) erroneously attack liver cells, they cause inflammation and damage to the liver. This results in the condition autoimmune hepatitis. There are two types of autoimmune hepatitis.
Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common type of the disease. Although it can affect anyone of any age, it most commonly develops in women aged around 45.
Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis primarily affects young girls between the ages of two and fourteen, and is much less common than type 1 hepatitis.
In many cases of autoimmune hepatitis the symptoms develop gradually over weeks or months. Often at the time of diagnosis there are very mild symptoms, or no symptoms at all.
How Autoimmune Hepatitis is Diagnosed
The presence of hepatitis is often discovered when patients are undergoing medical tests for unrelated disorders. Continue reading






